
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation comes from the sun and created sources such as welding torches and tanning beds. The term radiation refers to sending out energy from any type of source.
Types of UV Radiation
Scientists classify UV rays based on the amount of energy they contain. UV rays with the highest levels of energy create ionizing radiation, which means they can cause skin cancer by damaging the genes contained within cells. UV rays do not cause other types of cancer because they do not contain enough energy to penetrate past the skin. UV radiation comes in one of the following three types:
- UVC rays contain the greatest amount of radiation. Because of this, they are unable to reach the ground and do not pose a skin cancer risk. However, you may face exposure to UVC rays if you operate a blowtorch, a sanitizing light bulb that kills germs and bacteria, or a mercury lamp. Be sure to use these products sparingly and cover your skin when doing so.
- UVB rays are the primary cause of sunburn. They contain slightly less energy than UVC rays. Since UVB rays can cause direct damage to the DNA in skin cells, prolonged exposure to them increases the risk of skin cancer.
- UV rays contain the least amount of energy of all types of UV radiation. They are capable of causing indirect damage to the DNA of skin cells, such as premature skin aging. Although medical researchers believe that the main contribution of UV rays is wrinkled skin, they may contribute to the development of some types of skin cancer.
What Factors Influence the Intensity of UV Rays?
The sun’s rays are not always strong enough to reach the ground. Several factors contribute to their intensity level, including the following:
- Altitude: UV rays are more likely to reach the ground in higher altitude areas such as Colorado.
- Cloud cover: While more clouds in the sky make it more difficult for the sun’s rays to reach the ground, they still can. Following commonsense sun-safety tips is essential regardless of the weather.
- Latitude: UV exposure risk decreases the further a location is from the equator.
- Season: Spring and summer carry the most significant risk for damage caused by UV rays.
- Surface reflections: Your exposure to UV rays can be more intense when the sun’s beams bounce off water, snow, sand, or pavement.
- Time: The sun’s UV rays are most intense between 10:00 a.m. and 4:00 p.m. daily.
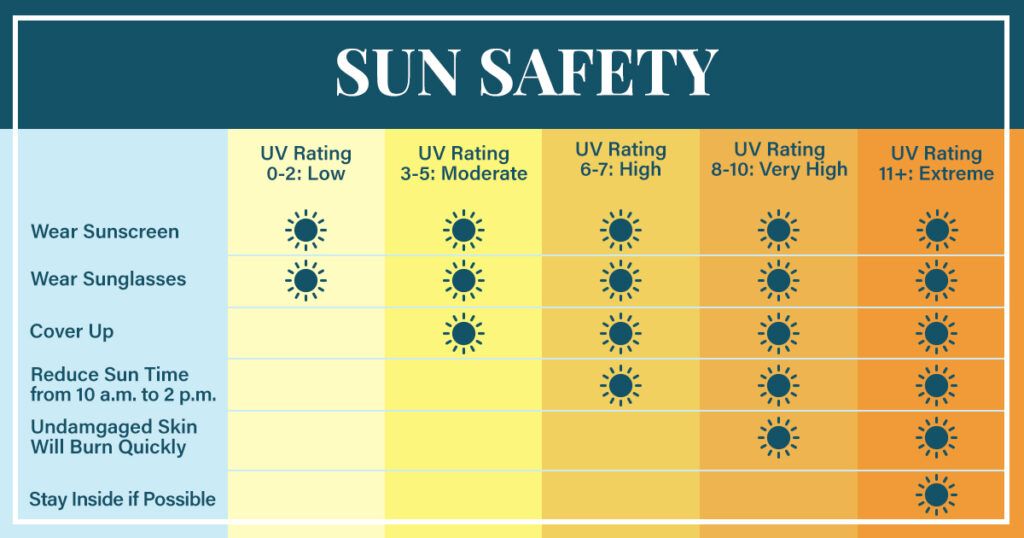
Try to make it a habit to listen to the US National Weather Service to learn the UV index each day. The UV index’s service rates from 1 to 11, and higher numbers represent an increased risk of damage caused by UV rays.
Please refer to our guide below for sun protection:
Health Problems Caused by UV Radiation
Besides skin cancer, sunburn, and premature skin aging, UV radiation can cause eye problems and weaken your immune system. When the eye’s cornea becomes inflamed, it can result in cataracts or pterygium, which is tissue growth inside the eye’s surface. Both conditions can significantly reduce or threaten vision. Exposure to UV radiation can even make the body have to fight harder against infections.
How to Protect Your Entire Body from UV Radiation
Sun safety starts with applying sunscreen every time you leave the house and reapplying every few hours while outdoors. You also want to wear lightweight clothing, sunglasses, and a hat that provides shade for your entire face. Avoid the hot sun by standing or sitting in the shade when you can, and try to avoid being in direct sunlight during the sun’s peak hours of intensity.
Please contact Anne Arundel Dermatology right away if you notice any changes in your skin, no matter how minor they may seem. If you need to stock up on sunscreen with a high SPF, use code SPF2021 to receive 10% off your purchase at our online store.































